Data science is rapidly transforming a wide range of industries by unlocking immense value from data, enabling informed decision-making, and powering cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning.
For individuals who are aspiring to enter this dynamic field or are currently in the early to mid stages of their careers, mastering the right set of data science skills is absolutely essential not only for gaining entry but also for advancing and thriving in this high-growth, competitive sector.
Given the rapid pace of technological advancements and the ever-increasing demand for skilled professionals, it can often feel overwhelming to determine which specific skills to prioritize and develop to stay relevant and successful in this evolving landscape.
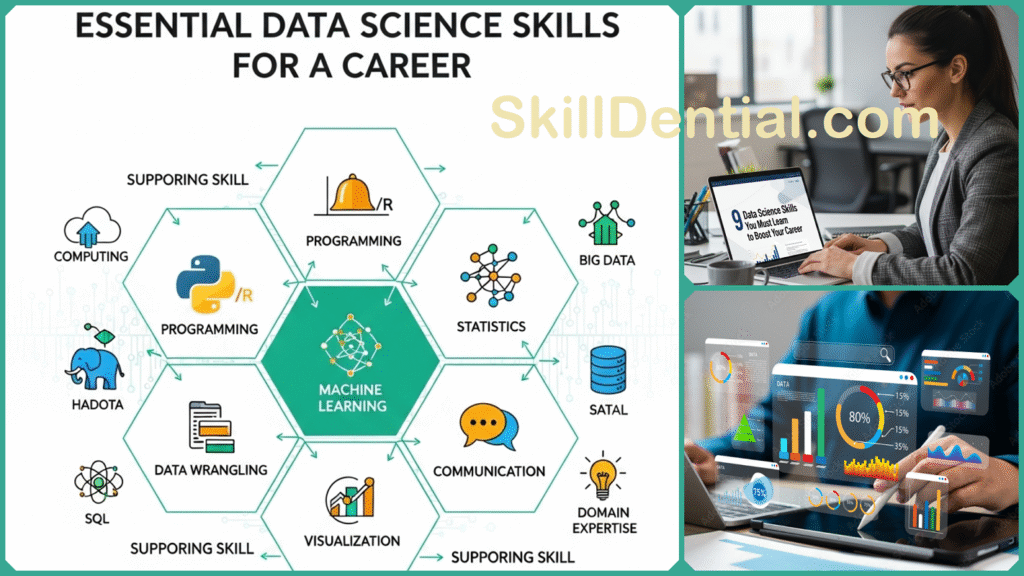
This blog post breaks down the often complex and rapidly evolving landscape of data science into nine essential skills that every data professional should focus on mastering to significantly boost their career prospects in 2025 and well beyond.
You will gain a clear and detailed understanding of what each skill specifically entails, why it holds critical importance in the data industry, and how it directly contributes to your overall success and effectiveness in various data-centric roles.
Whether you are currently a student eager to enter the field, a professional looking to make a career transition into data science, or a junior data scientist who wants to advance and level up your expertise, this comprehensive roadmap provides you with actionable and practical insights to help you make well-informed learning and career decisions with confidence.
Understanding Data Science
Data science is a highly interdisciplinary field that combines various scientific methods, processes, algorithms, and advanced systems to extract valuable knowledge and deep insights from both structured and unstructured data sources.
Essentially, it involves the complex process of transforming raw, unprocessed data into meaningful, actionable information that can be used to support decision-making and drive strategic initiatives.
Consider it as a combination that brings together several essential key areas:
- Statistics and Mathematics: This is the essential foundation upon which everything else is built. You rely heavily on statistical models and a wide range of mathematical concepts to thoroughly understand complex patterns, rigorously test hypotheses, and accurately make well-informed predictions. These tools form the backbone of analyzing and interpreting data effectively in various contexts.
- Computer Science and Programming: It is essential to have the ability to use various programming languages, such as Python and R, to effectively collect, clean, process, and analyze large and complex datasets. These skills enable you to handle data from multiple sources, ensuring it is accurate and ready for analysis. Additionally, you will use these programming abilities to build, train, and deploy predictive and analytical models, allowing you to extract valuable insights and solve real-world problems efficiently.
- Domain Expertise: This is absolutely crucial and cannot be overlooked. A data scientist must have a deep understanding of the context surrounding the data they are working with. For instance, a data scientist specializing in healthcare must possess a solid grasp of medical concepts, terminology, and practices to accurately interpret and analyze patient data. Without this essential domain knowledge, the insights and conclusions drawn from the data might be misleading or completely meaningless, as the data scientist would lack the necessary background to connect the data points to real-world implications.
The Data Science Life Cycle
Data science is not just a single task or activity; rather, it is a comprehensive process that involves multiple distinct stages, each playing a crucial role in the overall workflow:
- Data Capture/Collection: The process of gathering raw data from a wide variety of sources, including databases, websites, sensors, and many other input channels. This step involves collecting unprocessed information that serves as the foundation for further analysis and decision-making in various applications.
- Data Cleaning/Wrangling: This is an extremely important and substantial part of the job. It involves carefully identifying and handling missing values, removing duplicates, and resolving inconsistencies within the dataset to ensure the data becomes clean, reliable, and fully usable for further analysis.
- Data Exploration and Analysis (EDA): Thoroughly exploring the dataset to gain a deep understanding of its underlying characteristics, uncover significant patterns, and generate insightful hypotheses. This process frequently includes the creation of various visualizations such as charts, graphs, and plots to effectively illustrate the data’s trends and relationships, making it easier to interpret and analyze.
- Modeling and Machine Learning: Utilizing advanced algorithms and computational techniques to develop predictive models capable of accurately forecasting future trends and patterns. These models are also designed to effectively classify various types of information, enabling better decision-making and insights across multiple domains.
- Communication and Visualization: Effectively presenting the findings to stakeholders in a clear and easily understandable manner, often through detailed reports, interactive dashboards, or compelling and visually engaging visualizations that help straightforwardly convey complex information. This approach ensures that all parties can grasp the insights and make informed decisions based on the data presented.
Why is Data Science Important?
In today’s rapidly evolving world, organizations are increasingly overwhelmed by the enormous and ever-growing volumes of data generated every second. Data science offers powerful tools, advanced techniques, and systematic methods to analyze, interpret, and make sense of this vast sea of information.
By leveraging data science, businesses and organizations gain the ability to extract valuable insights and patterns, which can be used effectively to guide and support informed decision-making processes. It empowers businesses and organizations to:
- Make better predictions: Accurately forecast future sales figures, anticipate customer behavior patterns with greater precision, and identify emerging market trends well in advance to stay ahead of the competition.
- Improve decision-making: Leverage comprehensive data-driven insights to significantly enhance and optimize various business strategies. These strategies can range from creating highly targeted and effective marketing campaigns to streamlining and improving supply chain management processes, ultimately driving better overall business performance.
- Develop smarter products: Design and implement advanced recommendation systems similar to those used by Netflix or Amazon to provide personalized suggestions. Build sophisticated fraud detection systems that can identify unusual patterns and protect users from scams. Additionally, develop cutting-edge technology to power self-driving cars, enabling safer and more efficient transportation solutions.
- Innovate and solve complex problems: From accurately predicting disease outbreaks well in advance to optimizing energy grids for maximum efficiency, data science plays a central and indispensable role in tackling some of the world’s most pressing and complex challenges. It empowers researchers and professionals to analyze vast amounts of data, uncover hidden patterns, and develop innovative solutions that can significantly improve outcomes across various fields.
Key Data Science Skills You Must Learn
Mastering data science demands a diverse and comprehensive set of skills that extend well beyond the ability to write code alone. To genuinely succeed in this field and significantly advance your career, it is crucial to build a solid foundation in several key areas that are fundamental to the discipline.
The following skills are among the most highly sought-after by employers across various industries and will equip you with the essential tools and knowledge needed to effectively address and solve complex real-world data challenges with confidence and expertise.
Programming Proficiency (Python, R, SQL)
Programming serves as the essential foundation of data science, providing you with the tools and techniques necessary to effectively interact with, process, and analyze data. Among the various programming languages available, Python has become the most versatile and widely adopted option, largely due to its vast ecosystem of libraries and frameworks.
These include pandas, which is specifically designed for efficient data manipulation and analysis; scikit-learn, a powerful library that supports a wide range of machine learning algorithms; and matplotlib, which offers comprehensive capabilities for creating detailed and informative data visualizations.
On the other hand, when it comes to statistical modeling and academic research, the programming language R continues to be a strong and popular choice. It is particularly favored because of its extensive collection of packages that are specifically tailored for advanced data analysis, hypothesis testing, and statistical computing, making it a valuable tool for researchers and statisticians alike.
SQL, meanwhile, remains absolutely critical for querying, managing, and organizing relational databases—data that is stored in structured tables and forms the vast majority of business and organizational data. The ability to efficiently retrieve, manipulate, and analyze this data through SQL is considered an essential skill that cannot be overlooked or ignored.
Mastery of both Python and SQL is often explicitly stated as a requirement in nearly every data scientist job listing in 2025, clearly reflecting the widespread, industry-wide reliance on these powerful and versatile tools for data analysis and decision-making.
Statistics and Probability
A solid understanding of statistics and probability is absolutely fundamental for accurately interpreting data and making well-informed, evidence-based conclusions in a variety of fields. Key concepts, including hypothesis testing, regression analysis, probability distributions, and Bayesian inference, serve as the essential scientific foundation for validating predictive models and rigorously quantifying uncertainty in data-driven processes.
Employers place a high value on data professionals who possess the ability not only to execute statistical computations with precision but also to thoughtfully interpret and contextualize the results in a meaningful way that supports effective decision-making.
This strong statistical foundation is what truly distinguishes skilled data scientists who can adeptly navigate complex, multifaceted datasets and clearly communicate their findings to diverse stakeholders and decision-makers.
Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Machine learning (ML) techniques have increasingly become central to the process of extracting valuable predictive insights and automating a wide range of decision-making processes across various industries.
Developing a solid understanding and familiarity with classical algorithms, including linear regression, different classification methods such as decision trees and random forests, clustering techniques, and support vector machines, provides a strong foundation for progressing into more complex and advanced work in this field.
Deep learning, which is a specialized and rapidly growing subset of machine learning that focuses on neural networks with multiple layers, is becoming especially important for effectively handling and solving highly complex tasks such as natural language processing and computer vision, among many other challenging applications.
Popular and widely used frameworks such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn offer comprehensive tools and libraries that enable developers and data scientists to efficiently train, test, and fine-tune machine learning models for various applications.
Demonstrating proficiency and expertise in machine learning techniques and these frameworks significantly enhances career opportunities, opening the door to specialized roles that directly contribute to driving innovation and increasing revenue by delivering actionable, data-driven predictions and insights.
Data Wrangling and Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
Raw data is often messy, inconsistent, and frequently incomplete, making it difficult to use effectively in its original form. Data wrangling—the comprehensive process of cleaning, transforming, and preparing raw data—plays a crucial role in ensuring that the data is reliable and ready for accurate analysis.
In fact, it is estimated that roughly 80% of a data scientist’s time and effort is devoted to these essential preparation tasks, highlighting their importance in the overall data analysis workflow.
Exploratory Data Analysis is the crucial step that follows data wrangling and involves a comprehensive process of summarizing the key properties of the data, visualizing complex relationships between variables, and identifying any anomalies or outliers that could influence further investigations.
This stage is essential for gaining a deeper understanding of the dataset and guiding the direction of subsequent analysis. Powerful tools and libraries like pandas and NumPy provide robust support for efficient data manipulation and preparation, enabling analysts to clean and transform data effectively.
Meanwhile, advanced visualization libraries such as Seaborn and platforms like Power BI offer intuitive ways to create detailed visual representations that uncover underlying trends, patterns, and correlations within the data. Becoming proficient in this stage significantly accelerates the journey toward uncovering meaningful insights and making data-driven decisions.
Data Visualization and Storytelling
The ability to communicate data-driven insights clearly, effectively, and persuasively to a wide range of diverse audiences significantly elevates a data scientist’s overall impact and influence within an organization.
Tools such as Tableau, Power BI, matplotlib, and ggplot play a crucial role in facilitating the creation of visually appealing dashboards, detailed charts, and highly interactive reports that make complex data more accessible.
However, possessing technical prowess in visualization alone is not sufficient—when this technical skill is combined with strong storytelling abilities, it enables you to contextualize the results meaningfully, craft compelling narratives that highlight the significance of the findings, and ultimately guide well-informed business decisions with confidence and clarity.
Effective storytelling plays a crucial role in ensuring that valuable insights are not just identified but are also translated into practical, actionable strategies. Without this clear narrative approach, important information often remains buried within complex and overwhelming data sets, making it difficult for decision-makers to understand and apply the findings effectively.
By carefully crafting compelling and engaging stories around the available data, organizations can effectively bridge the often challenging gap between raw, unprocessed information and its practical, strategic implementation within the business framework.
Big Data Technologies
As organizations continue to handle ever-growing volumes of data, having a strong familiarity with big data platforms like Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark becomes increasingly essential. These advanced technologies enable the processing and detailed analysis of massive distributed data sets that far exceed the capacity and performance of traditional relational databases.
Additionally, major cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform offer robust, scalable infrastructures along with a wide range of specialized big data tools and services.
Consequently, possessing in-depth knowledge of cloud environments combined with expertise in big data architectures has become an exceptionally valuable and highly sought-after skill set in modern enterprise and business settings.
Cloud Computing and MLOps
Cloud computing has fundamentally transformed the field of data science by providing on-demand access to vast storage capabilities and powerful computational resources, which are essential for managing and processing large datasets as well as running complex machine learning models.
Understanding how to effectively leverage popular cloud platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform can significantly improve your ability to work efficiently and scale your projects seamlessly, allowing for more advanced data analysis and faster insights.
MLOps, which stands for Machine Learning Operations, is a rapidly emerging and increasingly important discipline that focuses on the seamless deployment, continuous monitoring, and effective maintenance of machine learning models within production environments.
Developing proficiency in MLOps practices is essential for ensuring that machine learning solutions remain not only reliable but also highly scalable and capable of continuous improvement over time. This discipline plays a critical role in bridging the often challenging gap between the development of data science models and their successful implementation in real-world applications and business processes.
Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
Data science encompasses much more than just possessing technical skills; it fundamentally involves the ability to frame and solve real-world business problems in a highly effective manner. Developing strong critical thinking skills empowers you to clearly articulate and define the problems at hand, thoughtfully generate and evaluate relevant hypotheses, design well-structured experiments, and carefully select the most appropriate methods and tools to extract meaningful insights from complex data sets.
This comprehensive skill set ensures that you do not simply apply algorithms blindly or mechanically but instead prioritize deriving practical, actionable, and data-driven solutions that can deliver significant and measurable value to organizations across various industries.
Communication and Collaboration
Cross-functional collaboration is absolutely intrinsic and essential to the success of data science projects, which frequently involve a diverse group of professionals, including data engineers, analysts, business decision-makers, and domain experts from various fields.
Having strong communication skills plays a crucial role in effectively synthesizing complex and technical insights into clear, accessible language. This approach not only facilitates greater buy-in from all stakeholders but also supports more informed and strategic decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
Additionally, a strong awareness of data privacy and ethical considerations plays a crucial role in fostering trust among colleagues and clients alike, ensuring the responsible and careful handling of sensitive and confidential information.
These interpersonal skills are absolutely vital for building cohesive, integrated teams and for effectively navigating the complex organizational environment, enabling smooth collaboration and communication across various departments.
Current Trends and Developments in Data Science Skills
Data science is an incredibly dynamic and fast-evolving field that is continuously shaped and transformed by rapid technological advancements and the ever-changing demands of various industries.
Keeping up to date with these emerging trends and developments is essential for professionals who want to stay competitive in the job market and continue to drive meaningful innovation within their organizations.
AI and Generative Models
The emergence of powerful AI models such as OpenAI’s GPT series and DALL·E has transformed the traditional role of data scientists. These generative AI systems can produce human-like text, create images, and assist in problem-solving, blending creativity with analytics.
For data scientists, integrating generative AI with conventional data models offers new avenues for innovation—from automated report generation to enhanced natural language processing (NLP) applications. Mastery of these AI tools expands your toolkit, positioning you at the forefront of next-generation data science.
Automated Machine Learning (AutoML)
AutoML platforms are gaining traction by automating repetitive aspects of machine learning pipelines, such as feature selection, model training, and hyperparameter tuning. While AutoML can accelerate model development, a deep understanding of machine learning principles remains crucial.
This expertise enables you to interpret AutoML outputs, customize models for specific use cases, and ensure robust, unbiased results. AutoML empowers data scientists to focus more on problem formulation and strategic insights rather than manual tuning.
Real-Time Analytics
The increasing demand for instant insights has pushed real-time analytics to the forefront of data science. Use cases like fraud detection in finance, monitoring IoT sensor data, and personalized e-commerce recommendations rely on analyzing data streams on the fly.
Technologies such as Apache Kafka and Apache Flink support processing continuous data flows, enabling rapid decision-making. Familiarity with these tools and concepts is becoming indispensable in environments where timely, data-driven actions confer a competitive edge.
Ethics and Data Privacy
Responsible use of data and AI is now a cornerstone of data science practice. Data scientists must navigate complex ethical considerations and comply with stringent privacy legislations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act).
Skills in ethical AI include bias detection, fairness auditing, transparency in model design, and rigorous data governance. Organizations increasingly prioritize trustworthiness in AI deployments to foster user confidence and meet regulatory requirements.
Continual Learning and Skill Adaptation
The data science landscape evolves quickly due to technological breakthroughs and shifting business priorities. To stay relevant, data professionals must commit to lifelong learning—whether through formal training, online courses, conferences, or self-study.
Skill adaptation includes updating technical expertise in new frameworks, tools, and methodologies, as well as enhancing soft skills such as communication and cross-disciplinary collaboration. A growth mindset and proactive upskilling are critical for sustained career progression in data science.
FAQs
What is the best programming language for beginners in data science?
Python is widely recommended for beginners due to its simplicity, readability, and extensive library support specifically for data science tasks (e.g., pandas, scikit-learn, TensorFlow). It offers versatility for both statistical analysis and machine learning. R remains valuable for specialized statistical work but has a steeper learning curve for general programming purposes. SQL is also fundamental for querying relational databases.
Do I need a strong math background to become a data scientist?
A solid understanding of statistics, probability, linear algebra, and calculus is crucial in data science. These areas underpin algorithm development, model interpretation, and statistical validation, ensuring your insights and predictions are robust and reliable. Employers prioritize candidates who can both apply mathematical concepts and explain their implications clearly.
How important is machine learning for data science careers?
Machine learning is essential as it enables building predictive models and automating data-driven insights. Most advanced data science roles demand at least foundational knowledge in supervised and unsupervised learning, along with familiarity with frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch. Deep learning skills further enhance your capabilities for complex problems such as image recognition and NLP.
Can I learn these skills online without formal education?
Many successful data scientists transition from diverse backgrounds using self-paced online courses, coding bootcamps, and hands-on projects. Consistency, practical application through real-world datasets, and continuous learning are key factors for success in this path.
What are the emerging skills in data science?
Emerging skills include MLOps (for deploying and monitoring ML models), proficiency in cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud), real-time data analytics, ethical AI practices focusing on fairness and privacy, and expertise in natural language processing (NLP). Staying updated with these areas is vital to keep pace with industry innovations.
In Conclusion
For aspiring and early-to-mid career professionals targeting data science roles, mastering the skills outlined above offers a clear, actionable roadmap to career growth. Programming, statistics, and machine learning form the technical foundation, while data wrangling, visualization, and big data tools expand practical capabilities.
Complementing these skills with a deep understanding of cloud technology, enhanced critical thinking abilities, and strong, effective communication prepares you thoroughly to thrive and excel in collaborative, dynamic, and high-impact professional environments.
The data science landscape is dynamic; staying current and continually sharpening these skills will unlock new opportunities, higher salaries, and job security. Start by focusing on one or two skills and gradually build expertise through hands-on projects and ongoing learning. This strategic approach positions you for success in one of today’s most exciting and rewarding fields.
Discover more from SkillDential
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


